- CompletableFuture
- 任务开启
- supplyAsync 开启一个子线程去执行有返回结果
- runAsync 开启一个子线程去执行无结果
- 任务结束
- get\join 获得返回值
- 串行任务
- thenApply\thenApplyAsync 串行将异步结果进行同步\异步的处理
- handle\handleAsync 允许有异常的情况下任然进行异步任务执行
- thenAccept\thenAcceptAsync 同步\异步穿行消费前任务无返回结果
- thenRun\thenRunAsync 不关注前任务的执行结果
- thenCompose\thenComposeAsync 允许多个任务Future流水线执行
- whenComplete\whenCompleteAsync 串行将异步结果进行同步\异步的处理
- 并行任务
- thenCombine 并列多任务执行并结果汇总
- thenAcceptBoth\thenAcceptBothAsync 并列多任务执行并消费结果无返回值
- applyToEither\applyToEitherAsync 两个任务并行进行用快的那个的结果作为后续处理
- runAfterBoth/runAfterBothAsync 两个任务都完成了不关注执行结果的进行下一步操作
- 任务开启
CompletableFuture
它代表某个同步或异步计算的一个阶段。你可以把它理解为是一个为了产生有价值最终结果的计算的流水线上的一个单元。这意味着多个指令可以链接起来从而一个阶段的完成可以触发下一个阶段的执行。
任务开启
supplyAsync 开启一个子线程去执行有返回结果
开启一个子线程用来执行执行事务,可以通过返回值的join来得到返回值.
例如:
print("去煮饭了");CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { print("煮饭中...."); sleep(); sleep(); sleep(); print("煮饭完成"); return "盛米饭";});sleep();print("炒完菜了");sleep();print(completableFuture.join()+"!开吃");返回结果:

runAsync 开启一个子线程去执行无结果
任务结束
get\join 获得返回值
join 隐性抛出异常、get显性抛出异常
Stopwatch stopwatch = Stopwatch.createStarted();CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 16 / 2);CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 27 / 3);try { Assertions.assertEquals(future1.get(),8);} catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace();} catch (ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace();}Assertions.assertEquals(future2.join(),9);串行任务
thenApply\thenApplyAsync 串行将异步结果进行同步\异步的处理
在当前阶段正常执行完成后(正常执行是指没有抛出异常)对前者的结果进行的操作。
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 16 / 2).thenApply(t1 -> t1*2);Assertions.assertEquals(future.join(),16);handle\handleAsync 允许有异常的情况下任然进行异步任务执行
handle 方法和 thenApply 方法处理方式基本一样。不同的是 handle 是在任务完成后再执行,还可以处理异常的任务。thenApply 只可以执行正常的任务,任务出现异常则不执行 thenApply 方法。
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 16 / 0).handle((t1, e) -> { System.out.println("handle=" + e.getMessage()); return Integer.MAX_VALUE;});Assertions.assertEquals(future.join(),Integer.MAX_VALUE);thenAccept\thenAcceptAsync 同步\异步穿行消费前任务无返回结果
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> getRemoteUser(familyName)) .thenAccept(list -> list.forEach(System.out::println));System.out.println(String.format("总执行耗时[%d]毫秒", stopwatch.elapsed(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)));future.join();thenRun\thenRunAsync 不关注前任务的执行结果
不关心任务的处理结果。只要上面的任务正确的执行完成,就开始执行。同样其也无返回值
CompletableFuture future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 12 / 1).thenRun(() -> System.out.println("无返回值的执行")); System.out.println(future.join());thenCompose\thenComposeAsync 允许多个任务Future流水线执行
允许你对两个任务进行流水线操作,第一个操作完成时,将其结果作为参数传递给第二个操作。你可以将多个任务嵌套的进行见例2
例1:
print("去煮饭了");CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { print("煮饭中...."); sleep(); sleep(); print("煮饭完成"); return "米饭";}).thenCompose(rice -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{ print("洗碗"); sleep(); print("洗碗洗完了"); return rice+"盛好了";}));sleep();print("炒完菜了");print(completableFuture.join()+"!开吃");返回结果:
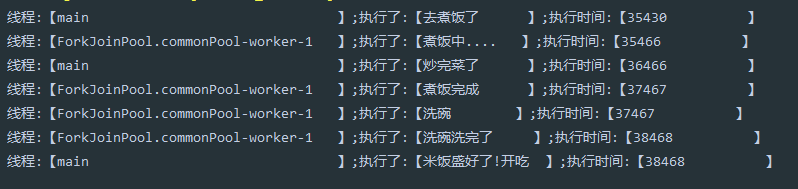
例2:
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 16 / 2) .thenComposeAsync(t1 -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> t1 / 2) .thenComposeAsync(t2 -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> t2 / 2)));Assertions.assertEquals(future.join(),2);结论:可以看出supplyAsync执行了异步方法,thenCompose将上一个异步的结果(文中的rice)拿到以后通过一个线程去执行了当前异步任务,并将结果在future.join()中输出了。
whenComplete\whenCompleteAsync 串行将异步结果进行同步\异步的处理
与thenAccept很像,区别在于whenComplete的执行会将前任务的返回结果给返回而thenAccept无返回结果。
//whenCompleteCompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 16 / 2);CompletableFuture<Integer> future = future1.whenComplete((t1, e) -> { Assertions.assertEquals(Thread.currentThread().getName(),"main"); Assertions.assertEquals(t1, 8); Assertions.assertNull(e); t1 = 10;});Assertions.assertEquals(future.join(), 8);//thenAcceptCompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 16 / 2);CompletableFuture<Void> future3 = future2.thenAccept(t1 -> { Assertions.assertEquals(Thread.currentThread().getName(), "main"); Assertions.assertEquals(t1, 8);});Assertions.assertNull(future3.join());//thenApplyCompletableFuture<Integer> future4 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 16 / 2);CompletableFuture<Integer> future5 = future4.thenApply(t1 -> { Assertions.assertEquals(Thread.currentThread().getName(), "main"); Assertions.assertEquals(t1, 8); return t1*2;});Assertions.assertEquals(future5.join(),16);System.out.println("------OK-------");并行任务
thenCombine 并列多任务执行并结果汇总
同时执行两个异步任务,并且在最后通过BiFunction将两个结果综合起来进行结果输出.
例如:
print("去煮饭了");CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { print("煮饭中...."); sleep(); sleep(); print("煮饭完成"); return "米饭";}).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{ print("洗碗"); sleep(); print("洗碗洗完了"); return "碗好了";}),(rice,bowl) -> { print("盛个饭"); return "盛个饭";});sleep();print("炒完菜了");print(completableFuture.join()+"!开吃");返回结果:

结论:可以看出supplyAsync执行了异步方法,thenCombine又起了一个新的线程并把两者的结果综合到一起(rice/bowl),由BiFunction进行计算,并将结果在future.join()中输出了。
thenAcceptBoth\thenAcceptBothAsync 并列多任务执行并消费结果无返回值
与thenCombine差不多,区别是thenAcceptBoth无返回值
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 16 / 2).thenApply(t1 -> t1/2);CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 27 / 3).thenApply(t1 -> t1/3);CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = future1.thenAcceptBoth(future2, (t1, t2) -> { Assertions.assertEquals(t1 + t2, 7);});completableFuture.join();applyToEither\applyToEitherAsync 两个任务并行进行用快的那个的结果作为后续处理
两个任务,谁执行返回的结果快,我就用那个任务的结果进行下一步的操作。
Stopwatch stopwatch = Stopwatch.createStarted();CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE); return 16 / 2;});CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 27 / 3);CompletableFuture<Integer> future = future1.applyToEither(future2, t -> t);Assertions.assertEquals(future.join(),9);Assertions.assertTrue(stopwatch.elapsed(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) < 1000);runAfterBoth/runAfterBothAsync 两个任务都完成了不关注执行结果的进行下一步操作
Stopwatch stopwatch = Stopwatch.createStarted();CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { sleep(2000); return 16 / 2;});CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 27 / 3);CompletableFuture<Void> future = future1.runAfterBothAsync(future2,() -> System.out.println("1234"));future.join();Assertions.assertTrue(stopwatch.elapsed(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) > 2000);原文转载:http://www.shaoqun.com/a/614585.html
tineye:https://www.ikjzd.com/w/448
斑马物流:https://www.ikjzd.com/w/1316
目录CompletableFuture任务开启supplyAsync开启一个子线程去执行有返回结果runAsync开启一个子线程去执行无结果任务结束get\join获得返回值串行任务thenApply\thenApplyAsync串行将异步结果进行同步\异步的处理handle\handleAsync允许有异常的情况下任然进行异步任务执行thenAccept\thenAcceptAsync同步\异步
tracker:https://www.ikjzd.com/w/2720
淘粉:https://www.ikjzd.com/w/1725
custommade:https://www.ikjzd.com/w/2514
喜大普奔!不打了!中美贸易战暂停,跨境电商卖家舒了一口气:https://www.ikjzd.com/home/12156
【Facebook】关于Facebook评论小技巧:https://www.ikjzd.com/tl/104780
口述:产权证无名分 她生完孩子找情人(2/2):http://lady.shaoqun.com/m/a/129501.html
No comments:
Post a Comment